Unveiling addiction and pregnancy statistics: Explore the risks, effects, and support for those facing this challenging journey.
Understanding Addiction and Pregnancy
Addiction and pregnancy is a complex and significant issue that has far-reaching implications for both the individual struggling with addiction and the developing baby. It is important to understand addiction as a public health issue and the impact of addiction on pregnancy.
Top 10 Statistics on Substance Use During Pregnancy:
- Approximately 5-10% of pregnant women in the US use illicit drugs during pregnancy.
- 30-60% of infants exposed to illicit drugs in utero will suffer from withdrawal symptoms.
- Alcohol is the most commonly used substance among pregnant women, with an estimated 10% of women drinking alcohol during pregnancy.
- Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) affect an estimated 2-5% of live births in the US each year.
- Smoking during pregnancy is associated with a 20-30% increased risk of preterm birth.
- Cannabis use during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk of stillbirth and low birth weight.
- Opioid use during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk of maternal and neonatal morbidity and mortality.
- Cocaine use during pregnancy increases the risk of placental abruption, which can be life-threatening for both the mother and baby.
- Methamphetamine use during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk of preterm birth, low birth weight, and neonatal withdrawal symptoms.
- Polydrug use (using multiple substances) is common among pregnant women who use drugs, and can increase the risk of adverse outcomes for both the mother and baby.

Addiction as a Public Health Issue
Addiction is a chronic disease that affects individuals from all walks of life, regardless of age, gender, or socioeconomic status. It is characterized by a compulsive and harmful dependence on substances or behaviors. Addiction not only has personal consequences for the individual but also has broader implications for society as a whole.
As a public health issue, addiction poses significant challenges in terms of healthcare costs, strained resources, and societal impact. It affects individuals, families, and communities, leading to increased rates of crime, unemployment, and mental health disorders. Understanding addiction as a public health issue helps to shift the focus from moral judgment to a compassionate approach that emphasizes prevention, treatment, and support.
The Impact of Addiction on Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a time of profound physical and emotional changes for women. When addiction is present, it can have serious consequences for both the mother and the developing baby. Substance use during pregnancy can lead to a range of health risks and complications.
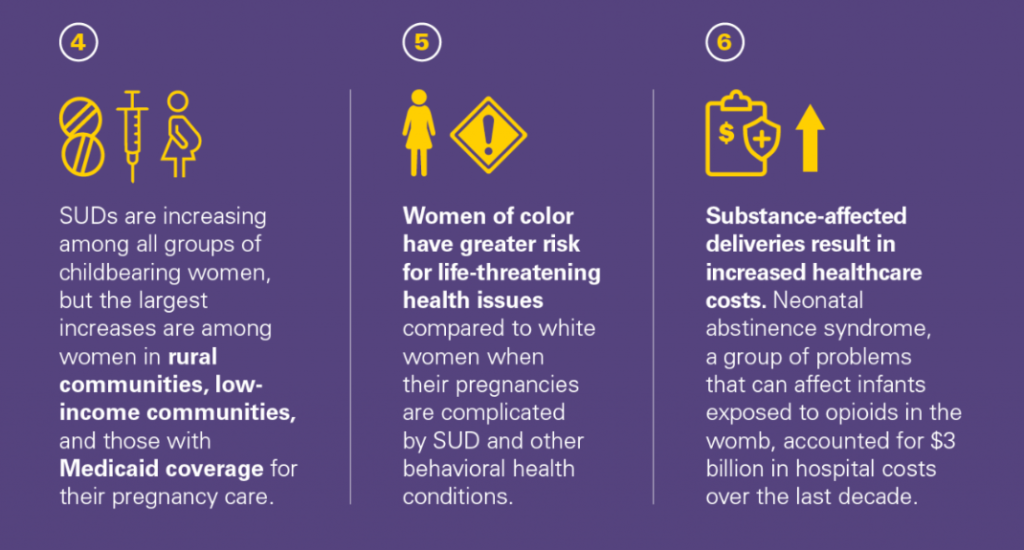
Prevalence of substance use during pregnancy varies depending on the substance and geographic location. It is essential to note that any substance use during pregnancy can pose potential risks. Commonly used substances include alcohol, tobacco, marijuana, opioids, and methamphetamine.
Substance use during pregnancy can lead to various risks and complications for both the mother and the baby. These include miscarriage, premature birth, low birth weight, developmental delays, neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS), and long-term developmental effects.
Understanding the impact of addiction on pregnancy is crucial for raising awareness, promoting prevention efforts, and ensuring that appropriate support and treatment options are available for women who are struggling with addiction during this critical time.
In the next section, we will delve into statistics on addiction and pregnancy, providing further insights into the prevalence of substance use during pregnancy and the associated risks and complications for both the mother and the baby.
Prevalence of Substance Use in Pregnancy
Substance use during pregnancy is a significant concern, as it can have detrimental effects on the health and well-being of both the mother and the developing baby. According to recent studies, approximately 5% to 10% of pregnant women use illicit drugs or misuse prescription medications during pregnancy. It’s important to note that this figure may vary depending on geographic location and population demographics.
To gain a deeper understanding of the specific substances commonly used during pregnancy, it’s crucial to analyze the data and statistics associated with each substance.
Risks and Complications for the Mother and Baby
Substance use during pregnancy can lead to various risks and complications for both the mother and the baby. These may include:
- Maternal health issues: Substance use during pregnancy can increase the risk of maternal complications such as poor nutrition, anemia, infections, and mental health disorders.
- Miscarriage: Substance abuse during pregnancy can increase the risk of miscarriage, particularly when certain substances like alcohol and illicit drugs are involved.
- Premature birth: Substance use during pregnancy is associated with a higher likelihood of premature birth, which can lead to a range of health issues for the baby.
- Low birth weight: Substance abuse during pregnancy can result in low birth weight, which is linked to developmental delays and long-term health problems for the baby.
- Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome (NAS): NAS occurs when babies are exposed to addictive substances in the womb, leading to withdrawal symptoms after birth. The prevalence of NAS varies, but it is estimated to affect approximately 6 out of 1,000 births.
By examining the prevalence of substance use during pregnancy, the commonly used substances, and the associated risks and complications, we can better understand the impact of addiction on both the mother and the developing baby. These statistics highlight the urgent need for support, treatment, and preventive measures to address addiction and protect the well-being of pregnant women and their babies.
Factors Contributing to Addiction and Pregnancy
When examining the complex relationship between addiction and pregnancy, it is important to understand the various factors that can contribute to this issue. These factors shed light on the challenges faced by individuals who find themselves in this situation. Some of the significant contributing factors include socioeconomic factors, lack of access to treatment and support, and co-occurring mental health disorders.
Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic factors play a significant role in addiction and pregnancy. Individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds may face additional challenges due to limited resources and opportunities. Economic instability, lack of education, unemployment, and poverty can increase the risk of substance abuse and addiction. The stressors associated with these factors can contribute to the development of addictive behaviors and make it difficult for individuals to seek the necessary help and support they need.
Lack of Access to Treatment and Support
Access to treatment and support is crucial for individuals struggling with addiction and pregnancy. Unfortunately, many individuals face barriers when trying to access adequate care. Limited availability of treatment facilities, long wait times, and financial constraints can prevent individuals from receiving the necessary help. Additionally, stigma surrounding addiction can discourage individuals from seeking assistance, further exacerbating the problem. It’s crucial to address these barriers and improve access to comprehensive treatment options and support services for those in need.
Co-occurring Mental Health Disorders
Co-occurring mental health disorders, such as anxiety, depression, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), frequently coexist with addiction and pregnancy. These disorders can contribute to the development and perpetuation of substance abuse issues. Individuals with untreated mental health conditions may turn to substances as a form of self-medication, using drugs or alcohol to alleviate emotional distress. It is essential to acknowledge and address the underlying mental health concerns alongside addiction in order to provide comprehensive and effective treatment.
Understanding the contributing factors to addiction and pregnancy is crucial in addressing this public health issue. By recognizing the impact of socioeconomic factors, advocating for improved access to treatment and support, and integrating mental health care, we can work towards reducing the prevalence of addiction during pregnancy and providing better outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
Effects of Addiction on the Developing Baby
When a pregnant individual struggles with addiction, the developing baby is also impacted. The effects of addiction on the fetus can be significant and have long-lasting consequences. In this section, we will explore two key aspects: Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome (NAS) and long-term developmental effects.
Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome (NAS)
Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome (NAS) is a condition that occurs when a baby is exposed to addictive substances during pregnancy. When a pregnant person uses substances such as opioids, benzodiazepines, or other drugs, these substances can pass through the placenta and affect the developing baby. After birth, when the baby is no longer exposed to the substance, they may experience withdrawal symptoms.
Common symptoms of NAS include excessive crying, irritability, tremors, poor feeding, and difficulty sleeping. The severity and duration of NAS symptoms can vary depending on factors such as the type of substance used, the duration of exposure, and the baby’s overall health. Prompt identification and appropriate medical care are essential to manage NAS effectively.
Long-term Developmental Effects
The impact of addiction on the developing baby can extend beyond the immediate withdrawal symptoms experienced with NAS. Prolonged substance exposure during pregnancy can have long-term developmental effects on the child. These effects may manifest in various areas, including physical, cognitive, and behavioral development.
Children exposed to substances in utero may face challenges in their physical growth and development. They may have a higher risk of experiencing delays in motor skills, speech and language development, and cognitive abilities. Additionally, behavioral issues, learning difficulties, and emotional regulation problems can be observed in some children affected by maternal substance use.
It’s important to note that each child’s experience may vary, and not all babies exposed to substances during pregnancy will face the same degree of developmental challenges. Early intervention, access to appropriate healthcare services, and a supportive environment can greatly contribute to minimizing the long-term effects on the child’s development.
Understanding the potential effects of addiction on the developing baby highlights the critical need for prevention, education, and support for pregnant individuals struggling with addiction. By providing comprehensive care and resources, we can strive to improve the outcomes for both the mother and the child.
Support and Treatment Options
When it comes to addressing addiction and pregnancy, it is crucial to provide comprehensive support and treatment options for expectant mothers. These options aim to promote the health and well-being of both the mother and the developing baby. Here are three key support and treatment options for women facing addiction during pregnancy:
Prenatal Care and Screening
Prenatal care plays a vital role in identifying and addressing addiction during pregnancy. Regular prenatal visits allow healthcare providers to monitor the mother’s health, assess potential risks, and provide appropriate interventions. Prenatal care also involves screening for substance use, including questions about drug and alcohol use, to identify any potential concerns. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve outcomes for both the mother and the baby.
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT)
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT) combines the use of medications with counseling and behavioral therapies to treat substance use disorders during pregnancy. MAT can be a highly effective approach for managing addiction and reducing the risks associated with substance use during pregnancy. Medications such as methadone or buprenorphine may be prescribed to stabilize the mother’s opioid dependence, ensuring a safer and more controlled withdrawal process. It is important to note that the use of medications during pregnancy should always be closely monitored by healthcare professionals to ensure both the mother’s and the baby’s safety.
Counseling and Support Programs
Counseling and support programs are crucial components of addiction treatment during pregnancy. These programs provide expectant mothers with the emotional support and coping strategies needed to address the underlying causes of addiction and develop healthier behaviors. Individual therapy, group therapy, and support groups tailored specifically for pregnant women can help address the unique challenges faced during this time. Counseling sessions may focus on relapse prevention, stress management, parenting skills, and building a strong support network. By participating in these programs, women can gain the necessary tools and support to overcome addiction and maintain their recovery journey.
By providing comprehensive support and treatment options like prenatal care and screening, medication-assisted treatment, and counseling programs, women facing addiction during pregnancy can receive the necessary care to promote their well-being and the health of their babies. It is essential to create an environment that encourages openness and seeks to address the underlying factors contributing to addiction, such as socioeconomic factors and co-occurring mental health disorders. With the right support, women can navigate the challenges of addiction and pregnancy with the hope of a healthier future for themselves and their children.
Conclusion
Addiction during pregnancy is a complex issue that requires a multifaceted approach to address. The statistics on the prevalence of substance use during pregnancy highlight the urgent need for comprehensive support and treatment options for pregnant individuals struggling with addiction. By examining the contributing factors, potential risks and complications, and available support and treatment options, we can work towards improving outcomes for both mothers and their babies.
It’s crucial to recognize that addiction is a treatable condition, and seeking help is a sign of strength. Early intervention, access to comprehensive care, and supportive environments are essential components of addressing addiction during pregnancy effectively. By prioritizing prevention efforts, advocating for improved access to treatment and support services, and reducing stigma surrounding addiction, we can work towards creating healthier futures for families impacted by addiction.
Sources
Substance Abuse and its Associated Factors
Effects of Drug Use During Pregnancy
Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome (NAS)



